Tensil Fabric Structures – Properties, Types and Advantages
Fabric tensile structures is a stretched fabric material in surface tension formed to a three-dimensional surface that can be used to create a roof, shading, or decorative component by tensioning it to cables and . It is constructed using a specialised fabrics under tension to support self-weight and take care of the live load providing a very cost effective and covering a large distances without intermediate supports.
A fabric material consists of three main components are fabric substrate, coating and top coating.
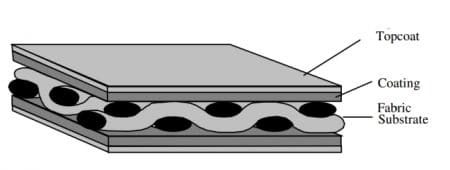
Fig 1: Main Component of Fabric Tensile Structure
In this article we study about the properties, types of fabric, types of top coating and advantages of fabric tensile structure.
Table of Contents
Properties of Fabrics for Tensile Structures
the different properties of a fabric which are considered for design are
1. Tensile Strength
It is a basic indicator of relative strength. It is fundamental for architectural fabrics that function primarily in tension.
2. Tear Strength
Tear strength is important in that if a fabric ruptures in place, it generally will do so by tearing.
3. Adhesion Strength
It is a measure of the strength of the bond between the base material and coating or film laminate that protects it. It is useful for evaluating the strength of welded joints for connecting strips of fabric into fabricated assembly.
4. Flame Retardancy
Fabric that contains a flame-retardant coating can withstand even a very hot point source. However, it can still burn if a large ignition source is present.
5. Flexibility
Free Form Tensile fabric allows one to use free form in building construction as it is flexible material.
Fig 2 : Flexible Fabric Umbrellas.
Types of Fabric Material for Tensile Structures
Fabric structures are composed of actual fabric rather than meshes or films. Typically, the fabric is coated and laminated with synthetic materials for increased strength, durability, and environmental resistance. Different type of fabrics used in tensile structures are,
1. Cotton Canvas
This is oldest n commonly used fabric material for the making of tents and shades on old days. It can be a light cotton twill, light canvas, or heavy proofed canvas.
2. Polyesters
The property of strength, durability, cost, and stretch make polyester material the most widely used in fabric structures. Polyesters that are laminated or coated with PVC films are usually the least expensive option for longer-term fabrications.
Polyester fabrics are futher divided into 2 types,
A. Vinyl-laminated polyesters
A laminated fabric usually is composed of a reinforcing polyester scrim pressed between two layers of unsupported PVC film. For most fabric structure uses, however, it refers to two or more layers of fabric or film joined by heat, pressure, and an adhesive to form a single ply.
B. Vinyl-coated polyester
Vinyl-coated polyester is made up of a polyester scrim, a bonding or adhesive agent, and exterior PVC coatings. It is the most frequently used material for flexible fabric structures.
3. Fiberglass
Woven fiberglass coated with PTFE is also a widely used base material. Glass fibres are drawn into continuous filaments, which are then bundled into yarns. The yarns are woven to form a substrate. The fiberglass carries a high ultimate tensile strength, behaves elastically, and does not suffer from significant stress relaxation or creep.
Because of its energy efficiency, high melting temperature and lack of creep, fiberglass-based fabrics have been the material of choice for stadium domes and other permanent structures.
Fiberglass fabrics are further divided into,
- Olefin / polyolefin fabric
- Polyvinylidene fluoride woven
- ePTFE woven
4. Blackout Fabric
Blackout fabric is a opaque material which consists of a laminate that sandwiches an opaque layer between two white exterior layers. Heating and lighting of a structure may be controlled because the fabric does not allow light to permeate the top or walls. The opaque quality also prevents stains, dirt, repairs, or slightly mismatched panels on the structure’s exterior from being noticed from the inside.
Types of Top Coating for Tensile Fabric Structures
Topcoating provides a hard surface on the outside of the material, forming a barrier that aids in preventing dirt from sticking to the material, while allowing the fabric to be cleaned with water. Based on the material used to topcoat the fabric, they are classified into following,
- PVF film lamination
- PVDF topcoating
- PVDF/PVC topcoating
- Tio2 (Titanium Dioxide) Top coating.
Advantages of Fabric Tensile Structure
- Quicker Installation
- Bright, Natural Diffused Day lighting
- Flexible Design Aesthetics
- Low Maintenance
- Lightweight Nature
- Energy Efficient
- Tensile Structures Need Less Materials
- Prefabrication Saves Time, Materials And Energy
- Wide Range Of Uses

No comments:
Post a Comment