Materials for Damp Proof Course in Construction
There are various types of materials for damp proof course used in construction works based on type of damp proofing required and type of structural element of building.
Damp proof course (DPC) is a barrier of impervious material built into a wall or pier to prevent moisture from moving to any part of the building.
Materials for damp proof course
Following are the materials generally used for damp proofing of structures:
1) Flexible Materials for Damp Proof Course
The materials, which do not crack and deform their shape when subjected to loading, are called Flexible Materials
a) Bitumen Mastic (Mastic Asphalt)
- It consists of asphalt or bitumen mixed with fine sand in hot state to form an impervious mass.
- Due to this consistency it can be spread (when hot) to a depth of 2.5cm to 5cm, which sets on cooling.
- It provides good impervious layer but special care is needed in its laying.
b) Bitumen Felts (Sheets)
- It consists of 6mm thick sheet of bitumen prepared in rolls having width equal to that of brick wall.
c) Hot laid Bitumen
This material is used on a bedding of cement concrete or mortar.
- This should be applied in two layers at the rate of 1.75kg/m2 of the area.
d) Metal Sheets
- Metal sheets of Copper, Aluminium, or Lead are used to prevent dampness, but they are costly.
- Sheets of these materials are used throughout the thickness of the wall.
- The sheets of Lead are laid over Lime Mortar and not with Cement.
- Mortar due to the chemical reaction of Cement over the Lead.
- The sheets of metal should be coated with asphalt.
- The thickness of the sheets should not be less than 3mm.
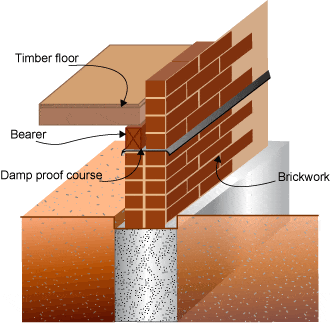
2) Rigid Materials for Damp Proof Course
- The materials, which do not resist transverse stresses and cracks when subjected to sever loading, are known as Rigid Materials.
a) Rich Concrete
- 1.2cm to 4cm thick layer of Rich Concrete (1:2:4) painted with two coats of hot bitumen is used as horizontal D.P.C.
- It also prevents the moisture penetration by capillary action.
- These layers are laid where the damp is not excessive.
b) Mortar:
- 2cm thick layer of Rich Cement and Sand Mortar (1:3) is applied on the inner face of external wall.
- This is a vertical D.P.C.
- The surface is than painted with two coats of hot bitumen.
c) Bricks:
- Over burnt or dense bricks in one or two layers can be used as cheap and effective DPC.
- They are laid in Rich Cement and Sand Mortar (1:3).
- Bricks are rarely used as DPC except in cheap houses.
d) Stones or Slates:
- Two layers of stone slabs or slates laid in Lime, Cement and Sand Mortar (1:1:6) make a best DPC.
- They can also be laid in Cement Sand Mortar.
- It is used where a good quality of stone is easily and cheaply available.
No comments:
Post a Comment