Types of Bitumen Mixes for Pavement Construction and their Applications
There are various types of bitumen mixes with aggregates for pavement construction. Applications of these bitumen mixes for pavements is discussed in this article.
Types of Bitumen Mixes for Pavement Construction and their Applications
Based on the nature of gradation selected for the bitumen mixes, they can be classified into:
- Dense Graded Bitumen Mixes
- Semi-Dense Graded Bitumen Mixes
- Open Graded Bitumen Mixes
- Gap Graded Bitumen Mixes
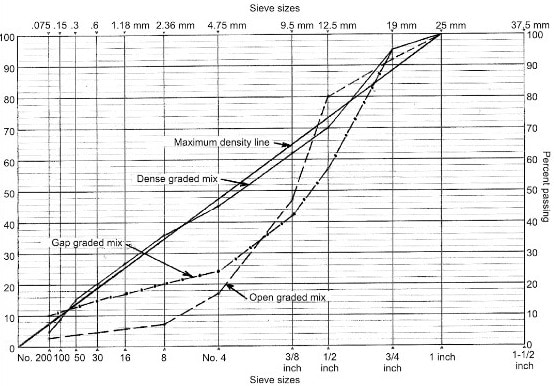
Fig.1: Gradation Chart for Dense, Open Graded and Gap Graded Bitumen Mixes Density
The bitumen mix that is densely graded has continuous gradation, say in the proximity of maximum density line. The bitumen mix with a large amount of fine aggregate i.e. sand will form open graded bitumen mix.
When the mix lack materials of two or more sizes, it will form gap graded bitumen mix. The semi-graded mix will have a gradation lying in between the open graded and the gap graded. All the gradation variations are represented in figure-1.

Dense Graded Bitumen Mixes for Pavements
These mixes possess continuous gradation of all primary aggregates. These particles are packed together. Here inter-particle surface friction is the reason behind their property of strength gain.
All most all possible flexible pavements constructed in the world employ dense graded bitumen mixes.
There are two main types of dense graded mix used. They are:
- Dense Bitumen Macadam (DBM)
- Bituminous Concrete(BC)
Dense Bitumen Mixes
This mix is mainly employed for base course and the binder course. This itself consist of two gradations; Grading-1 and Grading-2. Grading-1 has 37.5mm as the nominal maximum aggregate size (NMAS). While Grading-2 have NMAS of 25mm.
The fine aggregate percentages in both the grading are same in a range of 28 to 42%. The main criteria that differ both the grading are that the grading 1 consist of large size particles i.e. 25mm to 45mm.
The grading-1 with NMAS of 37.5mm has many disadvantages like segregation. This segregation will later result in honeycombing. At lower air-void levels, these mixes become permeable compared to the grading 2, with NMAS of 25mm.
Hence, the grading-1 causes problems related to water exposure. With the increase of NMAS, the permeability will increase the multi-fold at a present void level condition.

Fig.2: Dense Bitumen Mixes Grade-1, NMAS mix of 37.5mm -Honeycombing Defect due to Segregation
The effect of the nominal maximum aggregate size on the permeability of the flexible pavement is represented in the graph shown in figure-3.
The grade-1, have the advantage of rutting resistance compared to the grading-2. During the rainy season, the pavement made of NMAS 37.5MM, Grade 1 must be sealed or overlaid. This will avoid penetration of the water into the pavement and reach the Wet mix macadam. This is the WMM course also called as crushed stone base source.

Fig.3: Effect of Nominal Maximum Aggregate Size on Permeability of Flexible Pavement
Bituminous Concrete Mixes (BC)
The bituminous concrete mix is used in two forms: Grade-1 and Grade-2. Grade-1 with NMAS of 19mm. The Grade-2 of 13mm as the NMAS.
From the above description about dense bitumen mixes, it was clear that dense bitumen mix grade-2 have larger use as the base course due to its fewer disadvantages compared to dense bitumen mix Grade-1. This hence was necessary to determine a grade for the binder and the surface course.
The bituminous concrete grading-1 with nominal maximum aggregate size 19mm as the binder course binds the base course (dense bitumen mix Grade-1) as well as the wearing course bituminous concrete grade-2 of nominal maximum aggregate size 13mm, with NMAS 19 mm employed as a transition. The bituminous concrete grading-2 is good to be used as a wearing course.
To facilitate medium and low traffic, a bituminous concrete grade of nominal maximum aggregate size 9.5 mm was necessary to considered for the construction of smooth and impermeable pavement in urban areas.
To facilitate thin asphalt lifts, bituminous concrete grading-3 is more suitable than grade-2. The bituminous concrete grade-2 of NMAS 9.5mm has been efficiently used in the highway construction for the US. For higher traffic BC grade-2 are recommended.
Table-1: Recommended Bitumen Concrete(BC) Gradations

Semi-Dense Bitumen Mixes
The two types of semi-bituminous mixes used in the pavement construction in India are;
- Semi-Dense Bituminous Concrete (SDBC)
- Mixed Sealed Surfacing (MSS)
Semi-Dense Bituminous Concrete (SDBC)
The semi-dense bituminous concrete mixes have neither dense or open graded characteristics. It consists of the so called pessimum voids when they are fully constructed.
The word is an anonym of optimum. So, it is advised to make the mix get rid of pessimum voids. These tend to capture moisture or water that will later cause stripping.
When the semi dense bituminous concrete is employed above the bitumen macadam (BM) layer, there is chances for the penetration of rainwater through the SDBC and reach the BM.
This will create the separation of aggregate and the bitumen in the BM layer. This will cause stripping and the scaling of SDBC. The scaling later with time will result in the potholes on the road.

Fig.4: Semi-Dense Bituminous Concrete Highways with Shallow Potholes
Mixed Seal Surfacing (MSS)
The Mixed Seal Surfacing design mix is based on the IRC: SP:78-2008. This is an alternative used for the premix carpet (PMC). Both the PMC and the MSS are employed in 20mm thickness.
There are two gradations that are specified for the mixed seal surfacing mix. They are
- Type A – Closed Gradation with an NMAS value of 9.5mm
- Type B- Open Gradation with an NMAS value of 9.5mm or 12mm
The aggregate grading for the MSS mix is mentioned in table-2.
Table-2: Aggregate Grading for Mixed Seal Surfacing Mix

Open Graded Bitumen Mixes
The open graded Bitumen Mixes have fine aggregates in a minimum amount, hence they are very permeable to water. They are employed based on specific functions in the base and for surface mixes.
Open Graded Bitumen Base Mixes
Three open graded mix types are employed as the base mixes. They are the
- Asphalt Treated Permeable Base (ATPB)
- Bituminous Macadam(BM)
- Built up Spray Grout (BUSG)
Asphalt Treated Permeable Base (ATPB)
Permeable asphalt treated base (PATB) is used extensively on major highway construction in the US. This system will help to have sub surface drainage. The PATB is also called as the Asphalt Treated Permeable Base (ATPB). The system consists of separate course for the subsurface drainage. The thickness of the PATB ranges from 75mm to 100mm.
The PATB is given between the granular sub-base (GSB) and the bituminous course. The granular sub-base in flexible pavement too have the intention to provide subsurface drainage.
The GSB consist of large quantity of fines that are passing through 0.075mm sieve, which will let in providing excellent drainage system. A two-layer drainage system is implemented by this system.
Bituminous Macadam (BM)
The BM mix is open graded and highly permeable in nature. This is a recipe type mix produced that gain no kind of quality in terms of strength and volumetric. The void content is 20 to 25% higher than the dense graded bitumen (DBM). The DBM have a void content of 3 to 5%. The BM have high potential to attract water and moisture.
Built-up spray Grout (BUSG)
For flexible pavements, BUSG has been recommended as a base course. It is a two-layer composite construction with single size aggregates, which are nicely compacted. This has a hot bitumen layer applied after each layer. At the top, single sized key aggregate is applied.
As the sprayed bitumen does not help in filling the voids that are created by the coarse aggregate, these pavements behave to be highly permeable in nature. This does have a property to attract moisture and water. The application of BUSG as a remedy for the removal of potholes is stopped.
Open Graded Bitumen Surface Mixes
Three open graded mix types are employed as the surface mixes. They are:
- Open graded Friction course (OGFC)
- Premix Carpet (PMC)
- Surface Dressing
Open Graded Friction Course (OGFC)
The OGFC system consists of interconnected voids that help to improve the surface drainage property. Here the rainwater will drain through the OGFC and reach the bituminous concrete grade 2 (BC), that will later flow laterally within the OGFC. Which is later ended at the shoulder. The last OGFC layer will have a thickness of 20mm.
This system will have no trace of water on the surface. The OGFC system was developed in 2002, by the US nationals. The safety and the environmental features of OGFC are mentioned below:
- Improvement of frictional resistance of wet pavement
- Hydroplaning: Hydroplaning is the effect of skidding on ice and the loss of control problems of the vehicles. This is due to the presence of water during and after rain. The OGFC lets removal of water from the surface, letting no water trace on the pavement.
- The splash and the spray are reduced: The high-speed movement of vehicles will cause splashing and spraying of water to the nearby vehicles, which will cause problems to the visibility. The OGFC results in no water flooding in the road hence no splashing or spraying.
- Glare: The OGFC results in the reduction of glare from the headlights in the wet conditions. This will help in better visibility and have reduced driver fatigue.
- Noise Reduction
Premix Carpet (PC)
Here the PC is laid as a wearing course with a thickness of 20mm. The mix will compose two single size aggregates. One is the aggregate that is passing through 22.5mm and that will retain in 11.2mm.
The second aggregate type will pass through 13.2mm and retain on 5.6mm sieve. Here with respect to the climate and the traffic intensities, the viscosity grade bitumen are employed. It can be either VG-10 or VG-30.
Based on the aggregate and aggregate application rates that are specified in IRC: 14-2004, in “Recommended Practice for Open Graded Premix Carpet”, the bitumen content by weight of mix is 3.3%.
Surface Dressing
As per IRC:110 -2005, ” Specification and Code of Practice for Design AND Construction of Surface Dressing”, the surface dressing has the following significances and objectives:
- The surface dressing will provide a dust free wearing course over a granular base course that act similar to a water bound macadam (WBM) or a wet mixed Macadam (WMM).
- The surface Dressing will help in providing impermeability for water percolation for the road surface
- Surface Dressing provide high friction for the riding surface
- This will provide a renewal coat for periodic maintenance of bituminous wearing surfaces.
- The surface dressing work involves the process of spraying of proper grade paving bitumen mainly VG-10 or the rapid setting cationic emulsion. This is applied over an aggregate layer of appropriate size and gradation.
Surface dressing does not increase the structural strength and the riding quality of the pavement constructed.
Gap Graded Bitumen Mixes
The Stone Matrix Asphalt (SMA) is the most commonly used gap graded bituminous mixes. With the increasing traffic and the high pressure of tires of the vehicles will give large stresses to the road pavement. The roads are subjected to overloading conditions in certain cases.
The stone matrix asphalt mix is tough, highly stable in structure and rut resistant asphalt mix. These systems rely on the stone to stone contact that will facilitate in strength. The rich mortar used in the system will provide better durability.
The advantages of stone matrix asphalt mix are:
- Surface Frictional Resistance are improved
- The noise is reduced
- Compared to the conventional dense graded asphalt mix, the night visibility is reduced.
The following steps are involved in the stone matrix asphalt mix design:
- The selection of the materials i.e. aggregates, binder and the cellulose fiber.
- Three trial gradations are involved to ensure stone to stone contact.
- Optimum binder content is used for the all the gradation chosen
- The binder drains down as well as the moisture susceptibility is evaluated.
The performance of the stone matrix asphalt mix pavement as studied by the US, based on the rutting effect seen in the road pavement. The figure-5 below shows the rut depth caused for different ranges of the project conducted.

Fig.5: As per NCAT, the rutting performance of the stone matrix asphalt mix pavement constructed in the US
The performance of the SMA pavements that are constructed in India has performed well.
Compared to bitumen concrete, the cost for stone matrix asphalt mix has been found to be 25 to 30% higher. The increased cost of the SMA material is due to its composing materials like cellulose fiber, modified binder, and the binder content.
In the US, the life cycle study conducted showed that the stone matrix asphalt mix is more cost effective in terms of performance and lesser maintenance.

No comments:
Post a Comment