What are the Types of Ties Used in Building Construction?
Ties are tensioned reinforcements anchored and lapped mechanically or welded. Types of ties in building construction, their design and uses are discussed.
What are Ties in Building Construction?
Ties are continuous tensioned reinforcements which are completely anchored and sufficiently lapped mechanically or using weld. There are various types of building ties used for various purposes. These types of ties are shown in figure-1.
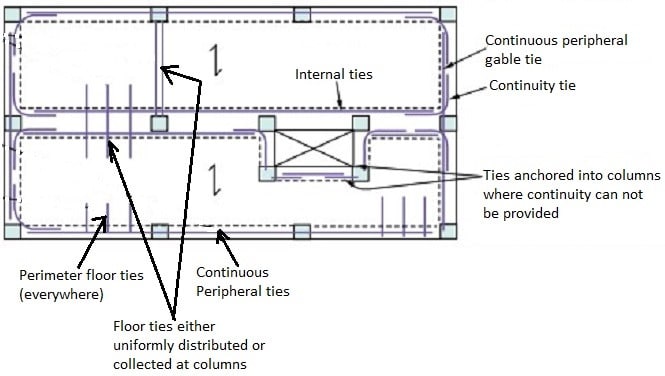
Fig.1: Different Types of Ties Used in Building Illustrated in a Typical Floor Plan
Types of Ties Used in Building Construction
Types of building ties include:
- Peripheral ties
- Internal ties
- Horizontal column and wall ties
- Vertical ties
Peripheral Ties in Building Construction
Peripheral ties are commonly provided at roof and floor level and it placed at 1.2m away from the perimeter wall or edge of the building, as explained in Figure-2.

Fig.2: Location of Peripheral Ties
peripheral ties must withstand a tensile force equal to the lesser of 60KN or an amount computed according to the following equation.
Ft = 20+4no -> Equation-1
Where:
n: is the number of storey of the structure
The area of steel bars required for the peripheral ties can be computed according to the following equation:
Ast=Ft / (0.87fy) -> Equation-2
Where:
Ast: is the steel area required for peripheral ties
Ft: Tensile force that peripheral tie should resist
Peripheral ties need to be anchored and lapped adequately. The location of peripheral ties need for a building is illustrated in Figure-3.

Fig.3: Location of peripheral ties are specified on typical floor plan
Internal Ties in Building Construction
Internal ties are placed at roof level and floor level in two directions nearly perpendicular to each other.
Internal ties should be effectively continuous along their length and connected at both ends to the peripheral ties or anchored to the columns or perimeter walls when such ties are continuous to columns or perimeter walls. Figure-4 illustrates the distribution of internal ties in typical floor plan
The maximum distance between internal ties is equal to the 1.5 times the longest distance between centers of vertical loading elements in the direction of ties.
The internal ties must withstand a tensile force equal or greater than the force computed according to the following formula:
Tensile force = 0.0267(gk+qk) lFt -> Equation-3
Where:
(gk+qk): is the sum of average characteristic dead load and live load exerted on the floor. These quantities are computed according to the specifications of Eurocode.

Fig.4: Distribution of Internal Ties in a Typical Floor of a Building
Vertical Ties in Building Construction
It is specified to use vertical ties for buildings with minimum five storeys. Each wall and each column that support vertical loads need to be continuously tied from lowest level (foundation) to highest level (roof of the structure).
If the utilization of vertical ties is not possible, then the element must be designed in such a way that if such member is removed, then the surrounding elements should be designed to be able to bridge the gap and prevent failure due the removal of that element.
The force that vertical ties are subjected to is equal to the maximum design ultimate dead load and live load exerted on walls or columns from any one storey.
Horizontal Ties to Column and Wall
These ties are used to connect external load bearing elements to the structure certain levels. Therefore, all external loads bearing members such as walls and columns are to be tied or anchored into structure at each roof or floor level horizontally.
The design tie force is equal to the greater of the two values computed according to the following expressions:
Design tie force = 2Ft or (floor to ceiling height in m / 2.5) Ft -> Equation-4
The smaller value is selected from equation-4
Design tie force = Three percent of the total ultimate vertical load in the wall or column at that level -> Equation-5
Horizontal ties should be provided in two directions at approximately right angle for corner columns.








