Steel Pile Foundations – Types, Design and Connections
Precast piles and driven cast in piles make use of steel pipes. In the case of precast or totally performed piles, there are two classification such as hollow small displacement piles and solid piles. The hollow small displacement piles make use of steel pipes when steel pile foundation is recommended. When it comes to solid piles, steel H- piles are used.
In the case of driven cast in place piles the main classification is concrete tube steel tube. In case of steel tubes, we make use of closed ended tube and open-ended tubes.
Generally, the steel piles can be classified as:
- Screw Piles
- Disc Piles
- H-piles
- Disc Piles
Commonly used steel piles are rolled steel H section piles or pipe piles. The pipe piles have either an open or a closed end that is driven into the ground. I-section or wide flange piles can also used as pile foundation.
The H-sections are preferred more over I-sections, as the H-section have same thickness for the web and the flange. In the case of I section, the thickness of the web is less compared to its flange thickness.
If Q is the allowable structural capacity, A being the cross – sectional area of the steel and the allowable stress of the steel given by fs, Then
Qall = A x fs
During the geotechnical investigation the design strength is determined as Qdesign and this must be within the Qall.
Connections in Steel Piles
The figure-1 below shows an H-pile being spliced by welding and riveting. Based on the requirement, the steel piles can be either welded or riveted for splicing purpose.
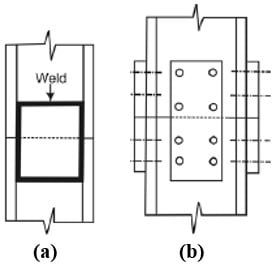
Fig.1: Splicing of H-Pile by means of (a)Welding (b) Rivets and Bolts
The pile ends as mentioned might have a flat bottom or a conical bottom as shown in the figure-3. Here welded connections are provided.

The piles are provided with driving shoes or driving points in order to facilitate easy movement in hard soils (Soft rock, shales and dense gravel). The figure-2 above forms two shoe types that can be provided for the piles.
Types of Steel Pile Foundations
1. Pipe Piles
Pipe piles are employed to behave as friction or end bearing piles. These piles are seamless and steel pipes that are formed by welding. The driving of these piles can be carried out with the help of an open or a close ended bottom. Hence, we have:
Open End Pipe Piles
These type of pipe piles is mostly used to penetrate a hard or a rock stratum. These piles after driving is sunk in the soil. The soil that is within the steel pipe is removed by means of compressed air or by means of water jetting process. After driving the steel pipe to required depth, the steel pipe is filled with concrete of standard specification.
Close End Pipe Piles
In this type of pipe piles, a conical element either made of steel or cast iron is attached to the open bottom by means of welding. This is the conical shoe. Once the pipe is driven into the soil, the pipe is filled with adequate amount of concrete.
The diameter of the pipe piles used can vary from 0.25m to 1.2m. The thickness of these pipe piles varies from 8 to 12mm. For pile foundation greater than 30 inches this type of pile works best.
2. Screw Piles
The screw piles are made of steel or cast iron. These form a long shaft that are terminating at the end in the form of a screw base or a helix. The shaft that is employed in the screw piles can be either a hollow one or a solid one.

Fig.3: Screw Piles
The base of the screw has a diameter ranging from 0.45 to 1.5m. The screw bottom is driven into the soil by means of an electric motor that help in easy penetration into the strata.
The screw piles have great application in clay or loose soils. Screw piles in these areas help in increasing the bearing area. The installation of pile foundation in these types of soils are made easy by the steel screw piling.
3. Disc Steel Piles
The disc steel pipe has an arrangement similar to the screw piles, where it has cast iron disc attached to the bottom. The pile sinks into the soil while penetration. So, to facilitate the water jetting process a hole is made at the bottom.
These types of piles can be employed in soft or sandy soil. This area is well suited as it allows the sinking of the disc piles during the water jetting process.
Disc piles are more applied for marine constructions, as these areas require for large amount of total penetration.
4. H-Piles
Rolled steel H-beams performed as a bearing pile is one of the new technology developed in the piling industry. Hard driving of the pile into the soil strata results in large amount of impact forces and stresses. The H-piles can sustain this stress to a large extent. H-piles are mostly used to penetrate an area with rock or any other hard strata.
No extra process of jetting, coring or adopting methods need to used to perform the penetration of H -piles. The small cross section of the H -piles make the soil displacement process easier.
Advantages of H-Piles
- H-piles consume less space for storage
- The handling of H-piles are performed easily
- H-piles penetration can be performed closer to the existing structure
- The amount of unusual displacement caused nearby area during the penetration of the H -piles are very small.
- The splicing process in H-piles can be performed easily.
- The maximum depth to which H-piles can be driven is 100m.
- H -piles perform the function of both friction and compaction piles
- The Main application of H -piles are in trestles, retaining walls, cofferdams and bridges.
Corrosion of Steel Piles
The steel pipes irrespective of what type is employed have great chance for corrosion. In such situations the piles can be coated with coal tar or corrosion protecting coating. Sometimes certain chemicals or materials are encased on concrete to prevent the corrosion.











 Fig.2: The main elements involved in a OPS technology in Bridge Construction
Fig.2: The main elements involved in a OPS technology in Bridge Construction