Hydrographic Surveying – Methods, Applications and Uses
Hydrographic surveying or bathymetric surveying is the survey of physical features present underwater. It is the science of measuring all factors beneath water that affect all the marine activities like dredging, marine constructions, offshore drilling etc.
Hydrographic surveying is mainly conducted under authority concerns. It is mainly carried out by means of sensors, sounding or electronic sensor system for shallow water.
The information obtained from hydrographic surveying is required to bring up nautical charts which involves,
- Available depths
- Improved Channels
- Breakwaters
- Piers
- The aids to navigation harbor facility
These survey also take part in necessary data collection relating to construction and developments of port facilities, such as pier construction. This help in finding the loss in capacity due to silt and many uncertainties.
Applications of Hydrographic Surveying
Following are the applications of hydrographic surveying:
- Dock and Harbor Engineering
- Irrigation
- River Works
- Land reclamation
- Water Power
- Flood Control
- Sewage Disposal
Uses of Hydrographic Surveying
Uses of hydrographic surveying are given below:
- Depth of the bed can be determined
- Shore lines can be determined
- Navigation Chart Preparation
- Locate sewer fall by measuring direct currents
- Locating mean sea level
- Scouring, silting and irregularities of the bed can be identified
- Tide measurement
- River and stream discharge measurement
- Massive structures like bridges, dams harbors are planned
Preliminary Steps in Hydrographic Surveying
The method starts by locating special control points along the shore line. The sounding method is employed to determine the depth at various points by means of stationary boats. Sounding locations can be either made from boat to the control points or by fixing a point in the boat and taking sounding from the control point. Before this procedure certain preliminary steps have to be made:
- Reconnaissance
- Locate Horizontal Control
- Locate vertical Control
Reconnaissance
As every project require a start-up plan to complete it effectively and economically, reconnaissance has to be undergone. A complete reconnaissance of whole survey area to choose the best way of performing the survey.
This would facilitate satisfactory completion of the survey in accordance with the requirements and specifications governing such work. Aerial photographs would help this study.
Locating Horizontal Control
The horizontal control is necessary to locate all features of the land and marine in true relative positions. Hence a series of lines whose lengths and azimuths are determined by means of either triangulation or any other methods.
Tachometric and plane table survey can be conducted in order to undergo rough works. No rules are kept for establishing horizontal control as topography, vegetation, type, size of topography affect the rules.
But in general a rules can be kept for type of control say:
- It is advisable to run traverses along each shore, connecting each other by frequent tie lines –If water body > 1km wide
- It is advisable to run transverse line only along one of the banks -If water body is narrow
- Triangulation system -If shorelines filled by vegetation
- Large network of triangulation system for large lakes and ocean shore lines
A combined triangulation and traversing is shown in figure 1.
Locating Vertical Control
Before sounding establishment of vertical control is essential to determined. Numerous benchmarks are placed in order to serve as vertical control. Setting and checking the levels of the gauges are uses of benchmarks

Fig. 1: Combined Triangulation and Traversing in Hydrographic Survey
Sounding in Hydrographic Survey
The process of determining depth below water surface is called as sounding. The step before undergoing sounding is determining the mean sea level. If the reduced level of any point of a water body is determined by subtracting the sounding from mean sea level, hence it is analogous to levelling.
The specific need for sounding are
1. Preparation of navigation charts that is an all-time information for future purpose also
2. Material that to be dredged has to be determined early to facilitate easy movement in project without any confusion
3. Material dredging should also accompany where filling has to be done. Material dumping is also measured
4. Design of backwaters, sea wells require detailed information that is obtained from sounding
Equipment for Sounding
The essential equipment used for undergoing sounding are
- Shore signals and buoys
- Sounding Equipment
- Instruments for measuring angles
The explanations are given below
1. Shore signal and buoys
These are required to mark the range lines. A line perpendicular to shore line obtained by line joining 2 or 3 signals in a straight line constitute the range line along which sounding has to be performed. Angular observations can also be made from sounding boats by this method. To make it visible from considerable distance in the sea it is made highly conspicuous.
A float made of light wood or air tight vessel which is weighted at bottom kept vertical by anchoring with guywires are called buoys. In order to accommodate a flag a hole is drilled. Under water deep, the range lines are marked by shore signals & the buoys.
2. Sounding Equipment
The individual units involved are explained one by one:
a. Sounding boat
A flat bottom of low draft is used to carry out sounding operation. Large size boats with motor are used for sounding in sea. The soundings are taken through wells provided in the boat. A figure depicting sounding boat is shown in fig.2.

Fig.2: Sounding Boat
b. Sounding pole or rod
Rod made of seasoned timber 5 to 10cm diameter and 5 to 8m length. A lead shoe of sufficient weight is connected at bottom to keep it vertical. Graduations are marked from bottom upwards. Hence readings on the rod corresponding to water surface is water depth.
c. Lead line
A graduated rope made of chain connected to the lead or sinker of 5 to 10kg, depending on current strength and water depth. Due to deep and swift flowing water variation will be there from true depth hence a correction is required.

Fig.3.Sounding Pole and Lead line
Other sounding equipment used are Weddell’s sounding machine. These are employed when large sounding work has to be undergone. A standard machine to measure maximum of 30 to 40m is designed that are bolted over the well of the sounding boat.
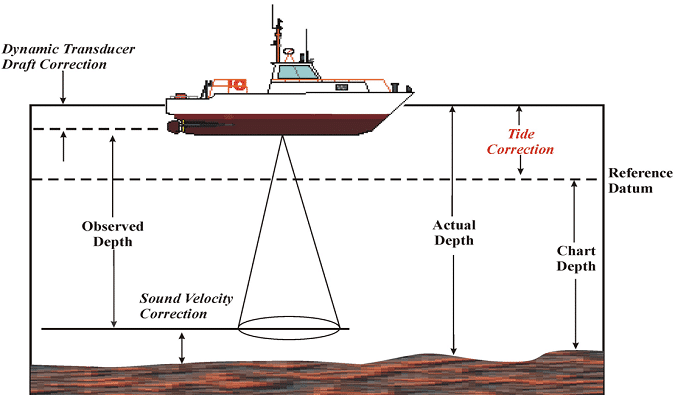
Another equipment used is fathometer which is an echo-sounding instrument used to determine ocean depth directly. Recording time of travel by sound waves is the principle employed. Here the time of travel from a point on the surface of the water to the bottom of the ocean and back is recorded.
Knowing the velocity of sound waves the depth can be calculated as shown in fig.4.

Fig.4: Echo Sounding in Hydrographic Survey
From the above figure the depth D can be calculated if AB can be found. This method gives truly vertical and accurate methods. It is found more sensitive than a lead line.