40+ Construction Tools List with Images for Building Construction
Construction tools list for building construction works such as concrete, brick masonry, leveling, wood works, floor works, slab works, brick laying, plastering etc. is provided. Every construction tool is necessary to achieve good results in the whole project.
Along with these tools, the workers should also use some safety tools to prevent them from the unexpected accidents.
Construction Tools List for Building Construction
Some important construction tools and their uses are listed below:
- Bolster
- Boning rod
- Brick hammer
- Bump cutter/screed
- Chisel
- Circular saw
- Concrete mixer
- Cordless drill
- Crowbar
- Digging bar
- End frames
- Float
- Gloves
- Hand saw
- Helmet
- Hoe
- Iron pan
- Jack plane
- Ladder
- Line and pins
- Mason’s square
- Measuring box
- Measuring tape
- Measuring wheel
- Pick axe
- Plumb bob
- Plumb rule
- Polishers
- Putty knife
- Rammer
- Rubber Boots
- Safety glasses
- Safety helmet
- Sand screen machine
- Scratchers
- Sledge hammer
- Spade
- Spirit level
- Straight edge brushes
- Tile cutter
- Trowel
- Vibrator
- Wedge
- Wheel barrow
Bolster
Bolster is like chisel but it is used to cut bricks. Its cutting edge is wider than the width of brick. It is useful for accurate cutting of bricks.

Boning Rods
Boning rods are made of wood and they are T shape. They are used to level the excavated trench throughout its length. Minimum three boning rods are used to level the trench surface.

Brick Hammer
Brick hammer is used to cut the bricks and also used to push the bricks if they come out of the course line.

Bump Cutter
Bump cutter is used to level the concrete surfaces like concrete floors, foundations etc. It is also called screed.

Chain Lewis and Pin Lewis
Chain lewis and pin lewis are two different tools which are used to lift heavy stones especially in the construction of stone masonry.

Chisel
Chisel is generally used in wood work and this must be useful to remove the concrete bumps or excess concrete in hardened surface.

Circular Saw
Circular saw used to cut the wood boards, frames etc. It is used when accurate cutting is required in less time. It is safer than hand saw.

Concrete Mixer
Concrete mixer is machine which mixes the ingredients water, fine aggregate, coarse aggregate and cement to deliver the perfectly mixed concrete.

Crowbar
Crowbar is used for digging the ground and to remove the roots of trees in the ground, nails etc.

Digging Bar
Digging bar is solid metal rod with pin shape at the bottom. It is also used to dig the hard surfaces of ground.

Drill Machine
Drill machine is used to make holes in the walls, slabs, doors, window frames etc.

End Frames
Their use is similar to the line and pins. But instead of pins, L shaped frames are used at the end of thread which hold the brick work effectively and level the alignment accurately.

Float
Float is made of wood which is used to smoothen the plastered concrete surface. It contains handle on its top and smooth wooden surface on its bottom.

Gloves
Gloves are required to prevent the hands from direct contact with cement, paints etc. and to avoid injury while using machines, tools etc.

Hand Saw
Hand saw is used to cut the wood materials like doors, windows, slab panels etc.

Head Pan
Head pan is made of iron which is used to lift the excavated soil or cement or concrete to the working site etc. it is more commonly used in construction sites.

Hoe
Hoe is also used to excavate the soil but in this case the metal plate is provided with acute angle to the wooden handle.

Jack Plane
Jack plane is used in the wood work to smoothen the surface of doors and windows etc.

Ladder
Ladder is also required in construction works. To check slab work, to transport material to the higher floors, to paint the walls etc.

Line and Pins
Line and pins consists a thread whose ends are connected with two solid metal rods with pin points. It is used to level the alignment of brick course while brick laying.

Mason’s Square
Mason’s square is used to achieve perfect right angle at the corner of masonry wall. It is “L” shape. First course is laid properly using Mason’s square then based on the first, remaining layers of bricks are set out.

Measuring Box
Measuring box is used to measure the quantity of sand and aggregate used for making concrete. It is of fixed dimensions so, aggregate need not to be weighted for every time. The general dimensions of a measuring box are 300mm X 300mm X 400mm (length x width x depth).
The volume of measuring box is generally 1 Cubic Feet, which makes it easy to measure concrete ratio or mortar ratio.

Measuring Tape
Measuring tape is used to check the thickness, length, widths of masonry walls, foundation beds, excavated trenches etc.

Measuring Wheel
Measuring wheel is used to measure the distances or lengths. It contains a wheel of known diameter, which record the no.of complete revolutions from which the distance can be measured. It makes the work easier.

Pick Axe
Pick axe is used to excavate the soil. It is more suitable for hard soil which is quite difficult to dig with spade or hoe.

Plumb Bob
Plumb bob is used to check the verticality of structures. It contains a solid metal bob connected to the end of a thread. It is also used inn surveying to level the instrument position.

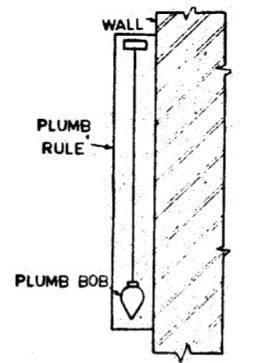
Plumb Rule
Plumb rule is used to check the vertical line of wall whether it is perfect vertical or not. It contains a straight wood board with uniform edges. On its center a groove is provided in which plumb bob is situated. When the rule is placed vertically with the wall the plumb bob should be in the groove line otherwise the wall will not be vertical.
Polisher
Polisher is used to smoothen the surface of tiles, wood works etc. The smoothening makes them shine and the process is called polishing.

Putty Knife
Putty knife is used level the putty finishing and also used to reduce the thickness of finish when it is more thick.

Earth Rammer
After the excavation of ground, the lower surface may be uneven. To level the surface earth rammer is used. It contains big square shaped block at its end with which the ground is leveled.

Rubber Boots
During construction works, legs may damage due to contact with chemical materials like cement or physical accidents. So, for safety rubber shoes are required.

Safety Glasses
To prevent the eyes from dust, chemical actions of materials etc. safety glasses should be maintained.

Safety Helmet
The safety helmet should be necessary in construction works. Any material or structure may fall from height during construction work. So, to protect the head from injury or any fatal accident, this safety helmet should be used.

Sand Screen Machine
The fine aggregate used in concrete should not contain impurities or coarse particles. The sand screen machine is used to screen the sand or fine aggregate before mixing it with concrete. This screen is also used for screening fine sand for plastering work.

Scratchers
Plastering of a surface is carried out layer wise. Minimum 2 coats are necessary for plastering. To provide the good bond between the coats, bottom layer is scratched with a tool called scratchers.

Sledge Hammer
Sledge hammer is used when the ground is hard and contains rock layers. A large weighted metal head is provided at the wooden handle with which hard layers can be cracked, which makes easy for digging.

Spade
Spade is used to dig the soil for foundation trenches etc. It contains metal plate at the end of long wooden handle.

Spirit Level
Spirit level is made of wood or hard plastic with bubble tube in the middle. The bubble tube is filled with alcohol partially. So, the air bubble is formed in it.
Spirit level is used in brick masonry to check the level of the surface. The spirit level is placed on surface and bubble is checked. The surface is leveled when the bubble in the tube settles at middle of tube.

Straight Edge Brushes
Straight edge brushes are used to provide finishing to the plastered surface especially at corners and edges of walls.

Tile Cutter
Tile cutter is used to cut the tiles. Sometimes, normal tile size is larger than required at the corners where floor meets the wall in that case tile cutter is useful.

Trowel
Trowel is used to lift and apply the cement mortar in small quantities. It is made of steel and wooden handle is provided for holding. The ends of trowel may be pointed or bull nosed.

Vibrator
Vibrator is used to compact the concrete by this the air gaps are filled with water and workability varies without adding water to it.

Wedge
Wedge is a small hard metal blade which is used to cut the rock surfaces with the help of sledge hammer.

Wheel Barrow
Wheel barrow is used to transport bulk weights of materials like cement, sand, concrete mix etc. it contains one or two wheels at its front and two handles at its back which are used to push the wheel barrow.







