Vastu Shastra For Building Construction – Beliefs, Benefits,Tips and Limitations
Vastu Shastra is an ancient Indian science which capitalizes on the concept of prosperity. It links person’s health and happiness directly with layouts and construction of a building.
Promoters of Vastu Shastra propagate that it is most authentic and proven advice science. They say that nature consists of 5 basic elements such as energy of planets, air, water, fire and earth. Each carries its own set of dynamics and with vastu one’s home and business can be synchronized.
As per promoters of shastra it creates a tremendous impact over all facts of life, i.e., health, life, education, thinking, prosperity, marriage and peace of mind.
In fact “Vastu Shastra” is the science of the ancient “Vedic Ages” of India under the guidance of which one can construct building of structures on a particular plot of land. For some people these principles are still relevant today also. As per their belief the science of “Vastu Shastra” controls forces of gravity and magnetic power of the earth.
The major beliefs of Vastu Shastra are as follows:
- Existence of roads on the northern or eastern side of the house improves the health and progress of the members of the house. If a house has road on the 3 sides, its inhabitants suffer tension and tension related problems.
- When the digging is happening to lay the foundation, make sure that you start from the east, go to the north, then to the west, and lastly, southwest.
- The plot at the end of a road is also not good for its inhabitants.
- It is good to have main door on east, northern and north eastern corner of the house. A house having main door at the southwest end provides less peace and perpetually tense atmosphere.
- A house having massive main door gives a lot of unsavory events and members residing suffer health problems.
- There should be no doors in the southwest corners or the southwest portion of the house. It is best if the doors face north or east. Doors should also open inside and not outside. When the door opens inside, it stands for inviting popular powers and positive energy. However, the door opening outside would be bad for the positive energy- it would actually drive the good energy away.
- Wall of house should have soothing and soft colors on walls as this gives a tension free atmosphere. Deep yellow, red or orange colored walls give irritation to the occupants.
- All water related appliances or resources of the house should be placed on north east area. This provides prosperity.
- A well or a tube well should never be provide on the southeast end of the house. A well or tube well at center of the house brings good luck to its head.
- Presence of plants of Tulsi, Banana, Champa, Ashoka, Aawla outside the house keeps inhabitants healthy, happy and peaceful.
Tips of Vastu Shastra for Building Construction
In the urban areas, due to the scarcity of land the construction of flats has become a common practice. Flats are economical and have some added benefit such as security, common recreation centers, shopping area etc.
Therefore, in urban areas purchase of flats are more common than constructing a house on a plot which becomes quite expensive.
In fact, construction of flats as per vastu is difficult still satisfactory results could be achieved if one follows principles of vastu meticulously in selection of plot and construction of buildings.
As per vastu experts, maximum benefits to the flat owners can be achieved keeping in mind the following principles of “Vastu”.
- The site should be a square or a rectangle. If possible southwest corner should have 90 degree.
- The main door should be on north, east or northeast side of the plot. 2 gates are preferable, one on east and other in the north. In addition to this northeast, southwest or northwest blocks are also good.
- Ground level should slope towards northeast and levels in southwest should be higher than all other sides.
- A bore well should be provided in north east before the construction takes place.
- More space should be provided in the east and north compared to west and south of the complex.
- Balcony towards north, east and northeast are preferable.
- Kitchen is advisable in south east or northwest but never in northeast.
- Staircase should be provided in the south, west or southwest and should be avoided in northeast because head room of the staircase higher than southwest is not acceptable.
- Underground room or space (cellar) should be kept under the northeastern or eastern portion of the complex.
- Parking for cars, scooter and bicycles are preferred in northeast cellar.
- Open area in north and south should be used for lawns and sumps.
- AC equipment should be kept in southeast of the complex and should never be installed in northeast under any circumstances.
- Washbasins should be provided in north or east or northeast of the hall.
Benefits of Vastu Shastra
One often thinks about how Vastu Shastra works and not enough about how they can benefit from the same. Here are some of the biggest benefits derived from Vastu Shastra to become successful:
- Comfort
- Inner realization
- Strength
- Easy to use
- Best use of space
- Good structuring
- Can enhance one’s personality
- Enhance relationship with other people
- Use this for spiritual knowledge
- Greater mental peace and skill
Limitations of Vastu Shastra
A general recommendation from vastu shastra has been provided for information of readers. While going through these recommendations they will conclude that most of the recommendations are governing the principles of good orientation and ventilation which are national building code also has recommended.
Since the principles of vastu are coming from Vedic period, to encourage people to get more benefits from nature, the principles have been associated mythological so the people will follow them.
Many examples could be cited to show that if principles of vastu followed in constructing one’s house one could be quite happy and prosperous.
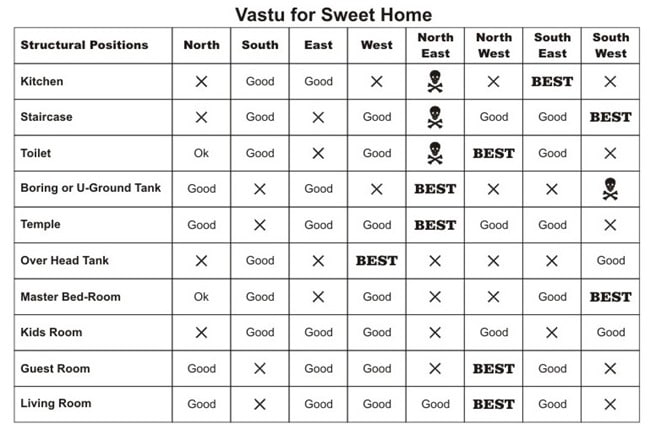
The figure above describes the best and worst position of rooms in house according to Vaastu.