Methods of Reinforcement Quantity Estimation in Concrete Structure
Estimation of steel reinforcement quantity is a necessary step in calculating cost of RCC structure along with other building materials as per construction drawing.
Accurate calculation of reinforcement in the building plays an important role in the over all costing of the project. The estimation of the reinforcement is made from the drawings and bar bending schedule.in the cases where there is no availability of drawings and schedules, the quantity is normally described in accordance with the requirements of the Standard method of measurement of building works.
Methods of Reinforcement Quantity Estimation:
There are different methods for estimating the quantities of reinforcement; three methods of varying accuracy are:
Method-1 : Reinforcement Estimation (Thumb Rule Method)
This simplest method is based on the type of structure and the volume of the reinforced concrete elements.
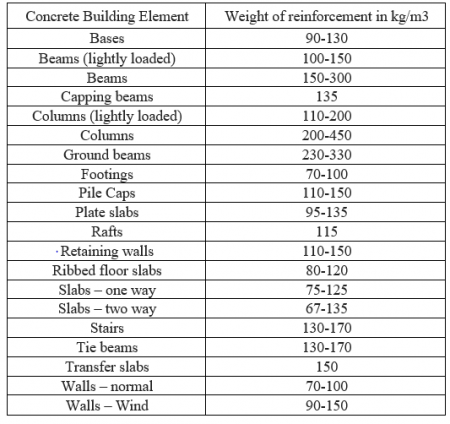
Average values for typical concrete frames:
Heavy industrial = 130 kg/m3
Commercial = 100 kg/m3
Institutional = 90 kg/m3
Commercial = 100 kg/m3
Institutional = 90 kg/m3
Residential = 85 kg/m3
However, while this simplest method to check on the total estimated quantity if reinforcement, same time it is the least accurate and it requires considerable experience to breakdown the tonnage down to Standard Method of Measurement requirements. Some of the elements breakdown is given below,
Standard Method of Measurement
Method-2 : Reinforcement Estimation (Accurate Method):
This is the most accurate method for quantity estimation of reinforcement. This method requires the drawings and schedules. The drawings used in this estimation are the representative of actual structure. The sketches include the intended form of detailing and distribution of main and secondary reinforcement. An allowance of additional steel for variations and holes may be made by inspection.
Let us take an example and estimate the quantity of reinforcement in method,

Reinforcement Details of a Typical Beam

Cross Section of a Typical Beam
Calculation:
Bar 1:
b = 4000 + (2 x 230) – (2 x 40) = 4380
No bends, hence, no deductions
Cutting Length = 4380 mm
Bar 2:
a = 200
b = 4000 + (2 x 230) – (2 x 40) = 4380
Deduction :
(2 x dia x no. of bends) = 2 x 20 x 2
Cutting Length = (2×200) + (4380) – (2 x 20 x 2) = 4700 mm
Bar 3:
a = 230 – (2×40) = 140
c = 375 – (2×40) = 285
Cutting Length:
(2A + 2C) + 24d = (2x 140 + 2x 285) + 24×8 = 1042 mm
No. of Stirrups: (4000/180) + 1 = 23.22 = 24

Bar Bending Schedule for the Beam
Number of bars:
Suppose the spacing of stirrups is 150 c/c and the length along which they are placed is 6800 mm, we can find the number of bars by the formula below
[ Length / Spacing] + 1 = number of bars
[ 6800 / 150] + 1 = 46.33
In this case, we always round up. Hence, we require 47 stirrups.
Cutting Length:
We must remember than steel is ductile in nature and is subject to elongation. Hence, the length of a bar is increased when bends or hooks are introduced. Hence, certain deductions are needed to offset this increase in length.
Cutting Length = True Length of a bar – Deductions
For 45 degree
Cutting length = Total length – 1 x Dia of bar x No. of bends
Cutting length = Total length – 1 x Dia of bar x No. of bends
For 90 degree
Cutting length = Total length – 2 x Dia of bar x No. of bends
Cutting length = Total length – 2 x Dia of bar x No. of bends
For stirrups:
90 degree hook:
Length of stirrup = (2A + 2B) + 20 x dia
135 degree hook:
Length of stirrup = (2A + 2B) + 24 x dia
Quantity Estimate for Reinforcement in Kg:

Quantity Estimation of Reinforcement in Kg
**Unit weight in kg/m is calculated using the formula = D2/162
For 8mm bar = 82/162
= 64/162
= 0.395 kg/m













 



